![[Home]](/images/httrack_header_title.gif)
Difference (from prior minor revision)
Changed: 3,4c3,4
< In HTTrack, use the following syntax for your URL(s):
< ##user:password@your.url##
to
> To handle this type of authentication with HTTrack, use the following syntax for your URL(s), with the username and password that you would normally enter in the browser popup window:
> ##username:password@your.url##
You can recognise HTTP Authentication when you access part of a website and your browser pops up a window prompting for username and password. Internet Explorer looks like:
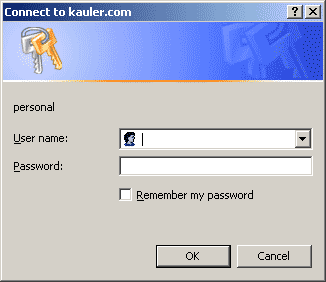
To handle this type of authentication with HTTrack, use the following syntax for your URL(s), with the username and password that you would normally enter in the browser popup window:
username:password@your.url
Example:
http://john:mypassword@www.example.com/private/page.html
If your username and/or password contains "special" characters you may have to replace (encode) them.
For example, if your username/password contains a '@' character, you should replace all '@' occurences with '%40' so that it can work: user%40domain.com:password@www.example.com/auth/.
Other characters include: